목록교내 수업 (29)
working_helen
 [R로 하는 통계분석] GAM(Generalized Additive Models)
[R로 하는 통계분석] GAM(Generalized Additive Models)
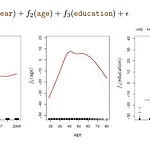
1. GAM (Generalized Additive Models)2. GAM R 코드로 구현하기 1. GAM (Generalized Additive Models)" 각 feature에 대한 비선형 함수를 선형결합 "= 각각의 설명변수 xj에 대해선 비선형 함수 fj(xij)를 적합 + fj(xij)들을 선형결합 - 각 fj는 glm, spline, identity 등 단일변수로 y를 예측하는 어떠한 모델이든 사용 가능 - linear additivity 유지함으로써 fj를 단순히 선형결합하여 최종 모델 적합 GAM regression 모델링 예시 `year` : natural spline, 자유도 4`age` : natural spline, 자유도 5 `education` : step function..
 [R로 하는 통계분석] Piecewise polynomial regression, Splines
[R로 하는 통계분석] Piecewise polynomial regression, Splines
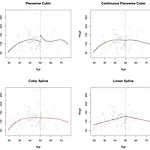
1. Piecewise polynomial regression2. Spline3. Spline R 코드로 구현하기 1. Piecewise polynomial regression(1) piecewise polynomial regression - 설명변수 X를 여러 개의 구간을 분할하고, 각 구간마다 별도의 다항회귀모형을 적합하는 방법 - 구간마다 각각 LSE를 적용해 회귀계수 β를 추정 - knots : 회귀모형이 바뀌는 X의 지점, K개의 knots가 있으면 K+1개의 구간이 생성 (2) basis function- piecewise polynomial regression은 basis function approach의 일종- 이미 알고있는 basis function(기저 함수) K개의 선형결합으..
 [R로 하는 통계분석] Classification 모델 적합과 평가
[R로 하는 통계분석] Classification 모델 적합과 평가
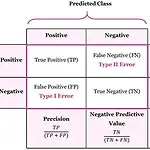
1. Logistic regression2. LDA3. QDA4. Naive Bayes model5. classification model evaluation 1. Logistic Regression: Binary Classification 반응변수 Y의 class가 0 또는 1 - q = P(Y=1) = E(Y) f(q) = logit(q) = log(q/(1- q)) = log(odds ratio) = Xβ- 주어진 x에 대한 결과 Y가 1이 될 확률의 예측값을 계산 예측된 확률에 적절한 threshold를 사용해 0 또는 1로 분류 (보통 0.5를 threshold로 사용) - β = logit(P(Y=1))의 변화량 = log(odds ratio)의 변화량 exp(β) = odds..
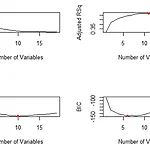 [R로 하는 통계분석] Linear Regression feature selection
[R로 하는 통계분석] Linear Regression feature selection
1. linear model fitting method2. subset selection 3. subset selection R 코드로 구현하기4. regularization 5. regularization R 코드로 구현하기 1. linear model fitting method - p개의 설명변수 X, 반응변수 Y - 기본적으로 linear model은 LSE(least square estimation) 방법으로 회귀계수 추정- 관측치 수가 충분히 많지 않거나 설명변수가 너무 많은 경우, 설명변수를 너무 많이 포함하면 과적합이 일어나고 model complexity가 증가 - LSE 대신 다른 model fitting 방법을 사용 subset selection : 전체 변수 중 일부만 사..
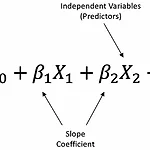 [R로 하는 통계분석] Linear Regression / GLM
[R로 하는 통계분석] Linear Regression / GLM
1. Generalized Linear Model(1) Logistic Regression(2) Poisson Regression(3) Negative Binomial Regression(4) Zero-inflated Poisson Regression 2. R 코드로 구현하기 1. Generalized Linear Model (GLM)Linear regression model은 선형성, 정규성, 등분산성, 독립성을 가정반응변수 Y가 정규분포를 따른다설명변수 X와 Y가 선형 관계에 있다 GLM= Linear regression model의 일반화= link function을 사용함으로써 더 다양한 종류의 분포를 따르는 Y를 X들 간 선형결합으로 표현할 수 있는 모델 Y가 정규분포를 포함하는 지수족(..
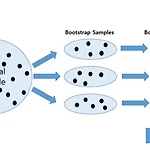 [R로 하는 통계분석] Bootstrap 신뢰구간 추정
[R로 하는 통계분석] Bootstrap 신뢰구간 추정
1. Bootstrap 2. R 코드로 구현하기 1. Bootstrap population → original sample → bootstrap smaples → bootstrap distribution - resampling from original sample without replacement - 현재 가지고 있는 original sample에서 복원추출을 통해 동일한 크기의 bootstrap samples를 생성 - bootstrap samples에서 원하는 통계량(statistics)를 계산하여 bootstrap distribution를 생성 ✅ origianl sample에서 bootstraping한 결과가 population에서 random smapling한 결과를 잘 근..
x - y 변수 종류에 따른 시각화 그래프 종류 Response (y)Explanatory (x)형태 Plot TypeR Function Numeric 연속형 x의 분포, y는 count/densityHistogram, Density plot `geom_histogram()`, `geom_density()` Categorical범주형 x의 분포, y는 count/propBarplot `geom_bar()` `geom_col()` NumericNumeric 연속형 x와 연속형 y의 분포산점도, 회귀선, 꺾은선 그래프, 면적 그래프`geom_point()`, `geom_smooth`, `geom_line`, `geom_bin2d()`Categorical Categorical 범주형 x와 범주형 y의 분..
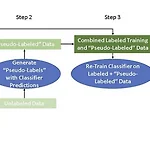 [ Week 11-2 ] with Insufficient Data / Semi-supervised learning, Active learning
[ Week 11-2 ] with Insufficient Data / Semi-supervised learning, Active learning
Lecture : Machine LearningDate : week 11, 2024/05/16Topic : With Insufficient Data 1. data augmentation2. Self training3. Active learning 1. data augmentation (데이터 증강)- expand labeled train data- 기존 데이터셋을 활용해 추가 합성 데이터를 인위로 생성하는 기법 - 데이터 셋의 규모를 키워 모델을 훈련에 필요한 충분한 수의 데이터를 확보하기 위해 사용 - 데이터 증강은 사용하는 데이터의 종류에 따라 특성이 달라지며, 다양한 기법이 존재한다. 2024.01.06 - [deep daiv./추천시스템 프로젝트] - [text 감정 추출 모델] Data A..
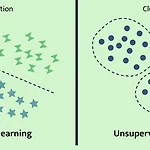 [ Week 11-1 ] Unsupervised learning / clustering, GMM, KDE
[ Week 11-1 ] Unsupervised learning / clustering, GMM, KDE
Lecture : Machine LearningDate : week 11, 2024/05/13 Topic : Unsupervised learning 1. Unsupervised learning 2. Clustering 3. k-means4. GMM5. KDE 1. Unsupervised learning Supervised learningUnsupervised learningtraining datausing labeled datasetusing unlabeled datasettrainmodel learns a function to relatebetween attributes and labels pairsmodel learns a function that producesuseful labels for..
 [ Week 9-1 ] Structured Classification
[ Week 9-1 ] Structured Classification
Lecture : Machine LearningDate : week 9, 2024/04/29Topic : Structured Classification 1. Markov chain & Markov model 2. Hidden Markov Model 3. Probability evaluation4. Optimal state sequence 1. Markov chain & Markov model 1) Markov chain(위키백과) 마르코프 연쇄(Markov chain)는 이산 시간 확률 과정이다. 마르코프 성질은 과거와 현재 상태가 주어졌을 때의 미래 상태의 조건부 확률 분포가 과거 상태와는 독립적으로 현재 상태에 의해서만 결정된다는 것을 뜻한다. 과거의 상태가 알려져 있더라도, 이는 미래 상태의..