working_helen
[ Week 2-2 ] Naive Bayes Model 본문
Lecture : Machine Learning
Date : week 2, 2024/03/07
Topic : Naive Bayes Model
1. Bayes' Rule
2. Naive Bayes Model
1) Model's Assumption
2) Model's Prediction
3) Smoothing
4) 장단점
3. Naive Bayes Model 예제
1. Bayes' Rule (베이즈 정리)
: 주어진 데이터로부터 Posterior Probability를 계산하기 위한 식

- X : Observation, 가지고 있는 instance 데이터
- Θ : Hypothesis, 데이터로 예측하려는 값
- P(X) : Marginal probability, likelihood of observing X in data
- P(Θ) : Prior probability(사전확률), belief in H before the observation
- P(X|Θ) : Likeihood, H가 참일때 likelihood of observing X
- P(Θ|X) : Posterior probability(사후확률), belief in H given observation X
2. Naive Bayes Model
(위키백과) 특성들 사이의 독립을 가정하는 베이즈 정리를 적용한 확률 분류기(Classification model)
1) Model's Assumption
different attributes are statistically independent given the classes
각 class 내에서 모든 attribute들의 확률은 서로 독립적이다
2) Model's prediction

- 사후확률을 가장 높게 만드는 class의 label로 분류하는 Classification Model
- 주어진 데이터 X에 대하여 각 class에 속할 사후확률을 계산하고, 값이 가장 높은 class로 분류하는 방식
- 사후확률을 계산하기 위해 베이즈 정리를 활용하며, 이때 모든 attributes 간 독립성을 가정
① Prior probability : 주어진 데이터로부터 각 class C에 속할 확률 계산
② Likeihood : 주어진 데이터로부터 각 class C 내서 X가 관측될 확률 계산
③ 데이터로부터 얻은 위 3가지 확률값과 베이지 정리를 통해 사후확률 계산
④ 사후확률 값이 가장 높은 class C로 X를 분류
3) Smoothing
Naive Bayes Model 문제점 : unobserved events의 사후확률 값이 0
==> Smoothing : treat unobserved events as possible but unlikely
- 훈련 데이터에 없는 event인 경우 사후 확률값이 0으로 계산됨
- 모든 Class 중 어느 하나라도 P(X|C) = 0 이면, 사후확률 값은 0이 되기 때문에
- 단지 기존 데이터에 없다는 이유로 현실에서 발생하지 않을 것으로 보는 문제
==> unobserved events에 매우 작은 발생 확률을 부과
① Simple Smoothing : 0을 ε(small positive constant)으로 대체하기
② Laplace Smoothing : 모든 event의 발생 횟수를 α(between 0 and 1)만큼 늘리기

4) 장단점
- 장점
- 모델 가정이 단순하고 생성이 쉬움
- 훈련시 데이터의 크기에 큰 영향을 받지 않아 큰 규모의 학습데이터에서도 잘 작동함
- 모델 결과의 이유를 이해하고 설명하기 쉬움 (Explainable)
- 단점
- P(X|C) 사전확률에 결측치가 많은 경우 정확도가 떨어짐
- attributes 간 독립성 가정이 적절하지 않은 경우에 부적합함
3. Naive Bayes Model 예제
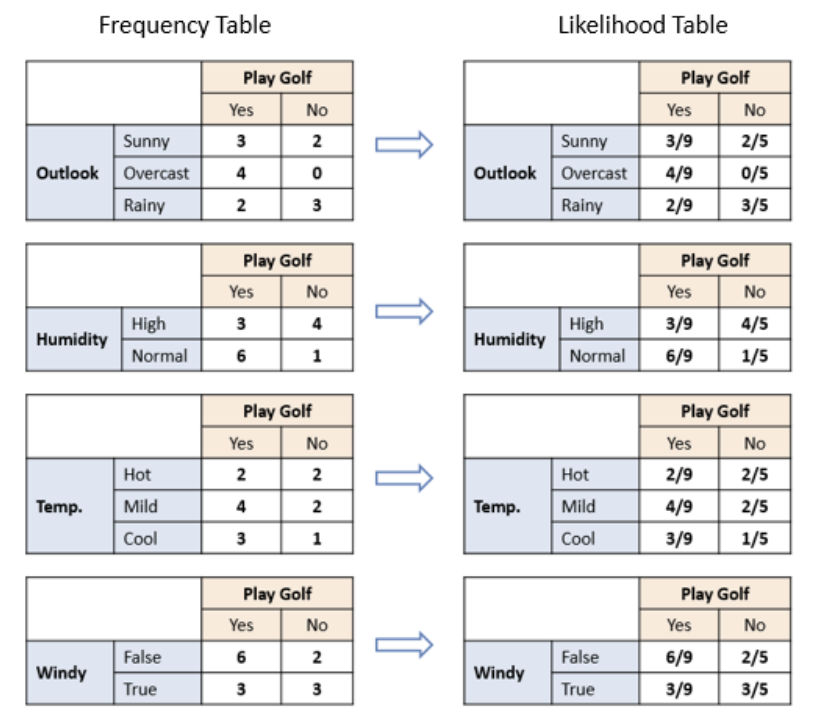
- train data : 14가지 instances
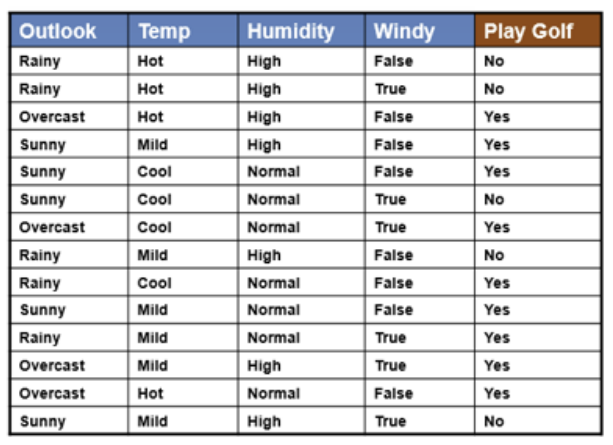
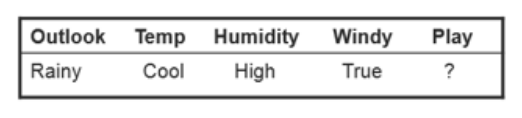
- test data
1) Prior probability 계산하기
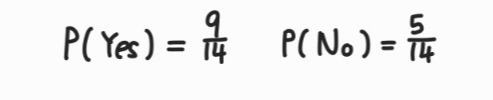
2) Likelihood 계산하기

3) Post probability 계산하기
- Naive Bayes Model의 가정 이용
- all features are independent given the class
all features are independent given the class

4) Label prediciton
- 사후확률 값이 더 높은 No로 분류
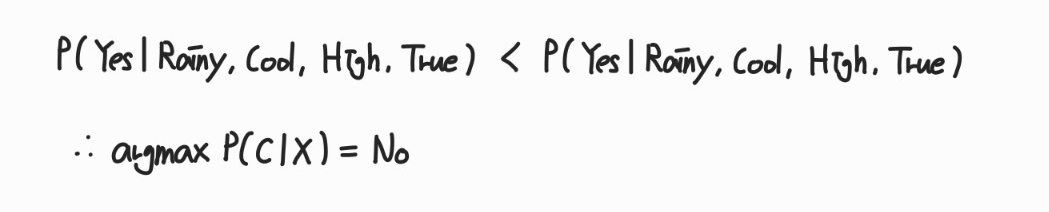
Reference
https://sanghyu.tistory.com/10
https://gsbang.tistory.com/entry/%EA%B8%B0%EA%B3%84%ED%95%99%EC%8A%B5-%EB%82%98%EC%9D%B4%EB%B8%8C-%EB%B2%A0%EC%9D%B4%EC%A6%88Naive-Bayes-%EC%9B%90%EB%A6%AC#recentComments
https://www.saedsayad.com/naive_bayesian.htm
'교내 수업 > Machine Learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [ Week 4-2 ] Decision Tree, ID3 algorithm (0) | 2024.03.25 |
|---|---|
| [ Week 3-2 ] Discretisation, Naive Bayes with continuous variable (0) | 2024.03.22 |
| [ Week 3-1 ] Instance-based Learning KNN (0) | 2024.03.18 |
| [ Week 2-1 ] types of attribute / probability / Entropy (3) | 2024.03.17 |
| [ Week 1 ] ML terminology / learning strategy (0) | 2024.03.17 |